Introduction
In an era dominated by rapid advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), the visual effects (VFX) industry finds itself at a crossroads. The integration of AI technologies has undeniably streamlined production processes, but it also raises profound questions about the potential moral implications and future role.
This article delves into the current state of AI in the VFX industry, explores its capabilities compared to human creativity, and considers the moral dimensions surrounding the collaboration between AI and VFX artists.
What’s the job of a VFX artist?
VFX artists are the creative architects behind the mesmerizing visual elements that enhance films, television shows, and various multimedia productions.
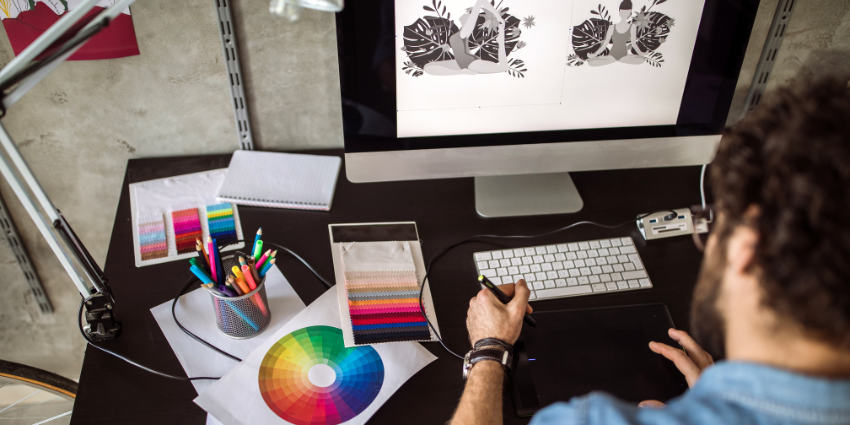

These skilled professionals utilize a diverse set of tools and techniques to seamlessly blend reality with the fantastical, crafting awe-inspiring scenes that captivate audiences. Their responsibilities encompass a wide range of tasks, including but not limited to compositing, 3D modeling, animation, texturing, and lighting.
VFX artists work closely with directors and cinematographers to bring their creative visions to life, often pushing the boundaries of what is visually possible. Whether creating otherworldly landscapes, designing intricate creatures, or executing complex visual sequences, VFX artists play a pivotal role in shaping the overall aesthetic and emotional impact of a production.
Beyond technical proficiency, these artists contribute their artistic intuition and storytelling prowess to ensure that the visual effects seamlessly integrate with the narrative, leaving a lasting impression on viewers.
What are different VFX artist positions?
The field of visual effects (VFX) encompasses a variety of specialized roles. Here are some common positions and job roles for VFX artists:
VFX Supervisor
Oversees the entire visual effects process, collaborating with directors, producers, and other departments to ensure that the visual effects align with the overall vision of the project.
Compositor
Responsible for combining various elements, such as live-action footage, CGI, and special effects, into a seamless and visually cohesive final product.
3D Modeler
Creates three-dimensional models of characters, objects, and environments using specialized software, often working closely with animators and texture artists.
Animator
Gives life to characters and objects by creating realistic movements and actions, whether through hand animation or motion-capture technology.
Texture Artist
Focuses on applying textures and materials to 3D models to achieve a realistic and visually appealing look, paying attention to details such as color, shading, and surface properties.
Lighting Artist
Designs and implements the lighting setup for scenes to evoke the desired mood and atmosphere, ensuring that the visual effects seamlessly integrate with the live-action elements.
Rigging Artist
Builds the skeletal structure (rig) for 3D characters, allowing animators to manipulate and control their movements precisely.
Effects Artist
Creates dynamic and realistic visual effects such as explosions, fire, smoke, and other natural or fantastical phenomena to enhance the cinematic experience.
Matte Painter
Produces images to be used as backgrounds or elements within a scene, helping to create expansive landscapes or environments that may not be feasible to film on location.
Pipeline Developer/Technical Director
Works on the technical aspects of the VFX production pipeline, developing tools and scripts to optimize workflows and ensure smooth collaboration between different departments.
Pre-visualization Artist (Previs)
Creates rough visual representations of scenes before they are filmed or fully animated, helping directors and producers plan and visualize complex sequences.
Matchmove Artist
Tracks and matches the movement of live-action elements with the corresponding CGI elements, ensuring accurate integration of visual effects into the scene.
These roles often require a combination of technical expertise, artistic skill, and a deep understanding of storytelling to contribute to the overall success of a project.
The Rise of AI in VFX
AI has ushered in transformative changes within the VFX landscape, offering indispensable tools that expedite production workflows. From automating repetitive tasks to optimizing rendering processes, AI has become integral to the VFX artist’s toolkit.
Companies in the entertainment industry increasingly rely on AI solutions to meet tight deadlines and deliver visual effects shots.

Automated Rotoscoping and Tracking
AI’s prowess is evident in areas such as rotoscoping and tracking, traditionally time-consuming tasks for VFX artists.
AI algorithms significantly reduce the time and effort required for these processes by automatically identifying and tracking objects in video footage. This accelerates production and enables artists to focus on more intricate and creative aspects of their work.
Facial Recognition and Animation
The lifelike characters seen in contemporary cinema owe a debt to AI advancements in facial recognition and animation. Deep learning algorithms can analyze facial expressions in real-time, providing a level of detail that was once painstakingly achieved by VFX artists.
The result is the seamless integration of CGI characters into live-action scenes, enhancing the overall realism of visual effects in movies and television.
Enhanced Rendering with AI
Rendering, a computationally intensive aspect of VFX, has seen marked improvements with the incorporation of AI. AI algorithms optimize rendering times by predicting final images based on partial information, reducing the need for extensive calculations.
This not only expedites the rendering process but also allows artists to iterate more rapidly, fostering enhanced creativity and experimentation.
AI as a Collaborative Tool
Despite these advancements, a prevailing perspective asserts that AI should be viewed as a collaborative tool rather than a replacement for human creativity. VFX artists bring a unique blend of artistic intuition, creativity, and storytelling that AI, at least for now, cannot replicate.
The subjective nature of artistic expression and the ability to make intuitive decisions based on emotion and narrative context remain distinctly human qualities.
The Moral Imperative of AI in VFX
As we navigate the fusion of AI and VFX, a moral imperative emerges. The ethical considerations of job displacement and the potential devaluation of human creativity cannot be ignored. While AI excels at automating tasks, it lacks the innate understanding of emotions, cultural nuances, and storytelling elements that human artists bring to their craft. The risk of reducing human creativity to a mere algorithm raises questions about the societal impact of AI in creative industries.
Can AI replace a VFX Artist?
The Human Touch in VFX
With the current AI technology is unlikely that AI will replace VFX artists completely. But there are tasks that can be done by AI in a more efficient way than humans.
An indispensable aspect of visual effects lies in the human touch that artists infuse into their creations. Whether designing fantastical worlds, crafting breathtaking landscapes, or evoking a specific mood through lighting and color grading, VFX artists bring a personal touch that resonates with audiences.

The human element is impossible to replicate through AI, which operates on predefined algorithms and learned patterns.
Limitations of AI
While artificial intelligence (AI) continues to advance rapidly, there are several nuanced skills inherent to human artists that remain challenging for AI to replicate.
These skills go beyond technical capabilities and touch upon the intricacies of creativity, emotional intelligence, and contextual understanding. Here are some skills that AI currently cannot fully replace in artists.
Creativity and Imagination
AI relies on patterns and data, lacking the innate ability to generate truly original and imaginative ideas. Human artists bring a unique creativity that involves intuition, inspiration, and the ability to think beyond predefined algorithms.
Emotional Intelligence
Understanding and conveying complex emotions, cultural nuances, and subtle nuances in storytelling are tasks that require emotional intelligence. AI lacks the genuine empathy and emotional understanding that human artists bring to their work.
Intuition and Instinct
Human artists often make intuitive decisions based on their instincts and gut feelings. This ability to trust one’s artistic instincts is challenging to replicate in an algorithmic system.
Adaptability and Innovation
Artists frequently encounter challenges that demand adaptability and innovation. The ability to experiment, take risks, and push boundaries in artistic expression is a uniquely human trait that goes beyond the capabilities of AI.
Subjectivity and Personal Perspective
Art is inherently subjective, shaped by an artist’s experiences, beliefs, and perspectives. AI lacks the subjective lens that human artists bring to their creations, making each piece of art a reflection of the individual behind it.
Aesthetic Judgment
Appreciating and making aesthetic judgments involves a complex interplay of personal taste, cultural influences, and artistic preferences. AI lacks the nuanced understanding required to make subjective aesthetic decisions.
Communication and Collaboration
Artistic projects often involve collaboration and effective communication. Human artists possess the ability to convey ideas, provide feedback, and collaborate with other creative professionals in a dynamic and intuitive manner.
Contextual Interpretation
Human artists excel at interpreting the broader context of a project, considering the emotional impact, cultural relevance, and intended message. This contextual interpretation is deeply ingrained in the artistic decision-making process.
Ethical Decision-Making
Artistic choices can carry ethical considerations, and human artists are equipped to navigate these complexities. AI lacks the moral compass and ethical reasoning required to make nuanced decisions in the realm of art.
While AI is a powerful tool that can enhance certain aspects of the creative process, the distinctive qualities and skills possessed by human artists continue to be essential for producing art that resonates on a profound and emotional level.
The collaboration between human creativity and AI innovation is likely to be the key to unlocking new possibilities in the artistic landscape.
Conclusion: The Indispensability of VFX Artists
In the ever-evolving landscape of AI and VFX, the collaborative future lies in recognizing the moral imperative of preserving human creativity. VFX artists are not merely technicians but storytellers, interpreters of emotion, and architects of immersive experiences. While AI continues to be a valuable tool in the industry, the importance of VFX artists cannot be overstated.
The fusion of human creativity and AI innovation, guided by ethical considerations, holds the key to pushing the boundaries of what is possible in visual effects. As we navigate this intersection, it becomes increasingly clear that VFX artists will always be indispensable.
The VFX artists’ ability to infuse projects with a uniquely human touch ensures that, despite technological advancements, the artistry and creativity of VFX professionals will remain at the heart of captivating storytelling and immersive cinematic experiences.

Nyx is an editor at Vertex Mode and a passionate 3D artist with years of experience in both gaming and film. With a deep love for digital art and visual storytelling, Nyx brings a unique blend of technical expertise and creative vision to every project. From sculpting detailed characters to designing immersive environments, their work reflects a commitment to pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in 3D design.
At Vertex Mode, Nyx not only oversees content but also shares valuable insights into the world of digital art and the creators behind it. They believe that every artist has a story worth telling, and through thoughtful articles and features, Nyx highlights the talent, challenges, and inspiration that shape the creative industry. Their perspective as a working 3D artist allows them to connect with readers in a way that feels both authentic and relatable.
Nyx’s expertise spans across concept development, modeling, and animation for both gaming and cinematic experiences. By blending artistry with technical precision, they continue to explore how digital tools can unlock new creative possibilities.
Through Vertex Mode, Nyx aims to inspire both aspiring and professional creators, offering resources, insights, and encouragement to thrive in the ever-evolving world of digital art.